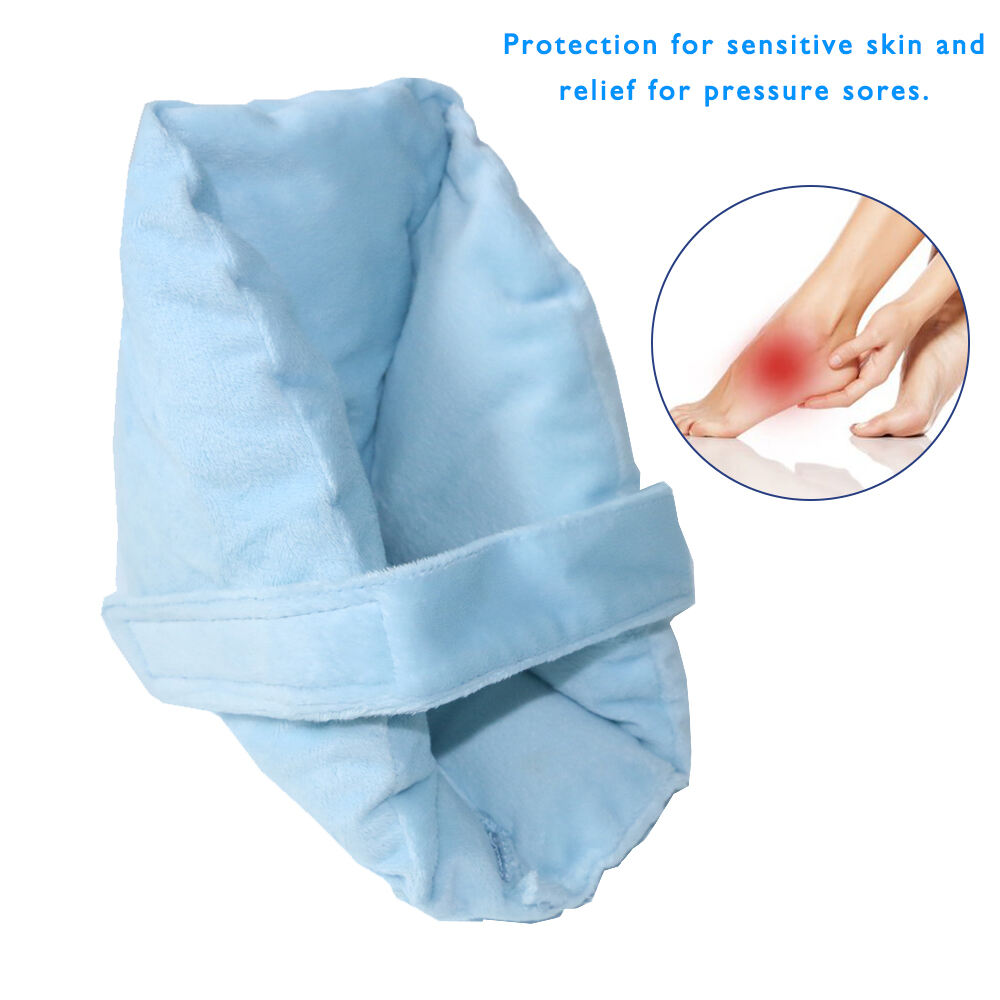
Understanding the Risk of Heel Pressure Sores
Why the Heel is Vulnerable
The heel's unique anatomy makes it particularly susceptible to pressure sores due to its bony prominence and minimal soft tissue coverage. Individuals with conditions like diabetes or vascular diseases face an even greater risk as these ailments compromise skin integrity, necessitating proactive preventative measures. Medical studies further reveal that those with limited mobility, such as bedridden patients, are at a heightened risk for developing heel pressure sores. This underscores the importance of comprehensive care plans that include regular mobility and pressure relief interventions.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the formation of heel pressure sores. Prolonged immobility is a major cause, as it increases pressure on areas like the heel. Additionally, external factors such as moisture from sweat or incontinence increase the risk of skin breakdown. Statistics indicate that elderly individuals in nursing homes are particularly vulnerable to these injuries. Therefore, it is essential to implement preventive strategies that include routine position changes and the use of appropriate heel pads and cushions to mitigate these risks effectively.
Spotting Early Symptoms: From Redness to Ulceration
Detecting early symptoms of heel pressure sores can prevent them from progressing to severe stages. Initial indicators, like localized redness, should prompt immediate assessment and intervention. Understanding the progression from non-blanching erythema to thickening and eventual ulceration is vital for effective preventive care. Regular skin assessments, especially for those at high risk, can significantly reduce the occurrence of advanced sores. Vigilance and timely responses are crucial in managing and preventing heel pressure ulcers.
How Heel Cushions Prevent Pressure Injuries
The Science of Offloading: Pressure Redistribution
Heel cushions are ingeniously designed to redistribute pressure away from the bony prominence of the heel, reducing the likelihood of skin breakdown. Research indicates that effective pressure redistribution can dramatically reduce the incidence of pressure injuries, contributing to improved patient outcomes and comfort. By incorporating heel cushions into care plans, healthcare facilities can not only enhance patient care but also lower the costs associated with treating pressure ulcers. Effective pressure management using these cushions thus becomes essential in both clinical and home settings, providing enhanced protection against heel pressure sores and maintaining skin integrity.
Reducing Friction and Shear Forces
One of the pivotal roles of heel cushions is minimizing friction between the heel and surfaces such as bedding, crucial for at-risk patients. These cushions are expertly crafted to mitigate friction and shear forces that can often exacerbate pressure injuries. Specialized heel pads designed for this purpose have been shown to outperform standard materials in clinical demonstrations, providing greater effectiveness in reducing shear. The reduction of these forces is essential, especially for patients with limited mobility who are more susceptible to skin damage, ensuring a comprehensive approach to heel injury prevention.
Complementing Repositioning Regimens
Heel cushions work best when used in conjunction with regular patient repositioning, forming an integral part of prevention strategies. Integrating these cushions into the daily care routine ensures consistent pressure relief and helps maintain skin integrity over time. Research underscores that comprehensive programs combining heel cushions and repositioning significantly reduce the occurrence of heel ulcers. Therefore, combining heel cushion integration with repositioning techniques offers an effective solution, enhancing overall prevention and care for individuals vulnerable to heel pressure injuries. This synergy between product usage and routine patient care reflects a holistic approach to managing heel pressure sores effectively.
Types and Selection of Heel Cushions
Constant Low Pressure (CLP) Pads vs. Offloading Devices
When choosing heel cushions, understanding the difference between Constant Low Pressure (CLP) pads and offloading devices is crucial. CLP pads are tailored for extended use, providing consistent support without increasing foot pressure. They are ideal for patients who need steady assistance. On the other hand, offloading devices actively lift the heel off any surface, which is crucial for patients at a higher risk of ulceration. The decision between these two options should be informed by the patient's mobility and their specific risk factors for pressure ulcers to ensure optimal patient care.
Key Features for Effective Protection
Selecting the right heel cushion involves considering features that ensure effective protection, such as breathability and moisture-wicking materials. These features help maintain skin health by reducing moisture build-up that can lead to skin breakdown. Cushions with adjustable firmness are beneficial as they allow customization to meet individual comfort levels and protection needs. According to clinical guidelines, choosing cushions that offer adequate support tailored to the patient's condition is vital, highlighting the importance of personalized care in preventing pressure injuries.
Positioning and Fit Considerations
Proper positioning and fit are essential for heel cushions to work effectively. The cushion should be positioned accurately to ensure the best pressure offloading and comfort. It must fit snugly, but not too tightly, to avoid cutting off circulation or causing any discomfort. Regular reassessment of cushion fit is essential, as a patient's condition and requirements may change over time, necessitating adjustments to continue providing optimal protection. Addressing these aspects ensures that heel cushions effectively prevent pressure injuries.
Through careful selection and application, heel cushions can play a significant role in preventing pressure ulcers, safeguarding patient well-being.
Implementing Comprehensive Heel Protection
NPIAP Guidelines: Assessment and Daily Skin Checks
Following the guidelines established by the National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel (NPIAP) is crucial in the standardized assessment of pressure injury risk, especially in caring for vulnerable patients. Daily skin checks play a vital role in catching early signs of pressure injuries, which is essential for preventing complications like heel ulcers. According to data, adherence to these assessment protocols significantly decreases the incidence rates of heel ulcers, underscoring the importance of early and regular monitoring. This proactive approach not only helps in early detection but also in crafting effective prevention strategies.
Integrating Cushions with Prophylactic Dressings
Using heel cushions in conjunction with prophylactic dressings offers an additional layer of protection against pressure injuries. This combination strategy is known to significantly enhance the overall effectiveness of injury prevention. Various studies indicate that the integration of cushions with dressings not only improves patient outcomes but also increases comfort. This approach helps distribute pressure more evenly across the heel, reducing stress on high-risk areas. As a result, patients experience fewer complications, demonstrating the value of such integrative techniques in comprehensive care plans.
Patient Compliance and Care Continuity
Educating patients about the importance of using heel cushions can dramatically improve compliance, which directly impacts the effectiveness of injury prevention efforts. Continuity of care, involving caregivers and healthcare providers, is vital for sustaining these protection strategies over time. Statistics support that when patients are actively engaged in their care plans, there is a significant reduction in complications. This emphasizes the need for ongoing education and communication among all parties involved, ensuring that the protective measures are consistently applied and adapted to changing patient needs.
FAQ Section
What are heel pressure sores?
Heel pressure sores are injuries to the skin and underlying tissue of the heel area, primarily caused by prolonged pressure. They occur due to the heel's bony prominence and lack of soft tissue, making it vulnerable, especially for individuals with limited mobility or compromised health.
How can heel pressure sores be prevented?
Prevention involves regular repositioning of the patient, using specialized heel cushions to redistribute pressure, and ensuring skin integrity through daily checks. Moisture-wicking and breathable materials can also help minimize risks.
What is the role of heel cushions in managing pressure sores?
Heel cushions play a pivotal role in pressure redistribution, reducing shear and friction, and complementing repositioning regimens, helping prevent the development of pressure injuries.
How do heel cushions integrate with other preventative measures?
They work best alongside repositioning regimens and prophylactic dressings, offering a comprehensive care approach that enhances protection and reduces the incidence of heel ulcers.
Why is patient compliance important in preventing heel pressure sores?
Patient compliance ensures that protective measures like heel cushions are properly used, which significantly reduces the risk of developing pressure injuries. Engaging patients and caregivers in care plans is crucial for sustained prevention efforts.

 EN
EN